Find Zenith and Azimuth angles
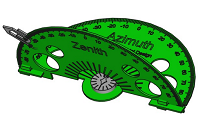
Navigating the Night Sky with Ease
The **3D-Compass** is an innovative physical tool designed to demystify spherical coordinates and empower high school students to locate stars and other celestial objects with accuracy. It transforms abstract astronomical concepts into a tangible, interactive experience.
This unique compass is constructed from **two semi-circle protractors**, each precisely graduated from -90° to +90°. These halves are cleverly folded along two planes perpendicular to each other, forming a three-dimensional representation of celestial coordinates.
- One protractor is dedicated to measuring **Declination** (similar to latitude in the sky, or Zenith angle).
- The other protractor is for **Right Ascension** (similar to longitude in the sky, or Horizon angle).
The Right Ascension half of the compass incorporates a **magnetic compass needle** for aligning with Earth's North, and the Declination half features a **sliding arrow pointer** that ultimately indicates the direction of the desired celestial object.
How to Locate a Star:
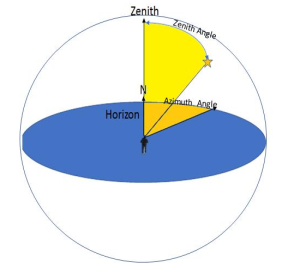
Using the 3D-Compass is a straightforward process once you know a star's coordinates:
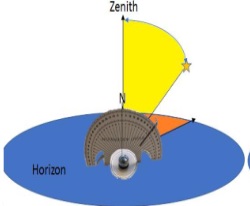
- **Align for Right Ascension:** First, align the magnetic compass needle on the Right Ascension half with the 90° mark.
- **Rotate Horizontally:** Gently rotate the entire 3D-Compass horizontally until the magnetic compass needle points to the specific **Right Ascension (RA) angle** of the star you wish to find. This action correctly positions the Declination half in the same plane as the star.
- **Set Declination:** Finally, slide the arrow pointer on the Declination half along its scale to match the star's **Declination angle**.
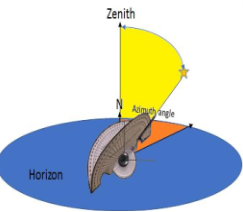
Once these steps are completed, the sliding arrow pointer will be pointing directly towards the star's location in the sky, making celestial navigation intuitive and exciting!
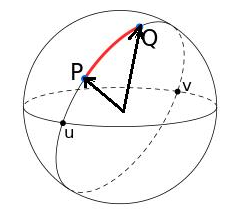
Understanding Your Tool
The 3D-Compass consists of two perpendicular semi-circle protractors (ranging from -90° to +90°):
1. The Azimuth/RA Base:The horizontal plane equipped with a magnetic compass to align with the Earth's poles.
2. The Zenith/Dec Arch:The vertical plane featuring a sliding pointer to target the altitude of the object.
Step-by-Step Guide
Object: Star Pollux
Zenith: 45°
Azimuth: -50°
01. Hold the 3D-Compass horizontally. Adjust the Zenith pointer on the vertical arch to 45°.
02. Align the 0° mark on the Azimuth base with the magnetic North needle.
03. Rotate the device horizontally until the compass needle points to -50° on the Azimuth scale.
The Zenith pointer now aligns perfectly with your target star.
User Tips
Sidereal time: is a timekeeping system, based on Earth's rotation relative to distant, fixed stars, not the Sun. A sidereal day is about 23 hours, 56 minutes, 4.1 seconds (roughly 4 minutes shorter than a solar day) and is the time for one full Earth rotation relative to these stars, visit USNO Sidereal Time Calculator web site or www.mathandastronomy.com/SiderealTime.
Celestial Coordinate system: a framework, like latitude and longitude for Earth, used to map positions of stars, galaxies, and other objects on the imaginary celestial sphere, The most common is the equatorial system, using declination (like latitude, north/south of the celestial equator) and right ascension (like longitude, east-west along the equator, measured in hours).
Zenith: the zenith is the imaginary point on the celestial sphere directly above an observer's head, 90 degrees up from the horizon
Azimuth: In astronomy, azimuth is the horizontal angle, measured clockwise from a reference direction (usually North, 0°) around the observer's horizon, it tells you the object's compass direction in the sky
Educational Advantages:
Spatial Reasoning
Develops crucial 3D spatial understanding for complex astronomical systems.
Hands-On Application
Provides a practical way for students to apply and visualize Right Ascension and Declination.
Conceptual Bridge
Helps students connect abstract coordinate data from star charts to the physical sky above them.
Engaging Astronomy
Transforms star-gazing into an interactive learning experience, sparking curiosity about the cosmos.
"The 3D-Compass: Guiding the next generation of astronomers to the wonders of the night sky!"
Learn More or Purchase